Character Encoding for WebPages: HTTP file headers
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the language used by a Web server and a Web browser to communicate with each other.
Every time a Web server serves a page to the browser, it adds an invisible "HTTP response header" to the file. This file header (not to be confused with the <head> section of a document) is metadata, which means it contains information about the file that it is serving to the browser. Many servers include character encoding (the character set used in the document) in this header. In other words, the server tells the browser how the document is encoded. (But, what the server says about the encoding may not be how the documents it serves are actually encoded; this is determined by your text editor when it saves a file.)
Most servers will say the files it serves are either ISO-8859-1 (Western European Latin characters) or the newer Unicode standard, UTF-8. In documents written in English there is little difference between these two standards; most noticeable differences will be in special punctuation. But if you wish to have your Web page display more than Western European languages (perhaps a page that mixes English with Chinese, for example), you cannot use ISO-8859-1; UTF-8 would be the way to go. At any rate, UTF-8 is the current standard for Web pages.
Browsers (also called "user agents") use an "HTTP request header" when requesting a file from the server. In this request header the browser identifies itself with a "user agent string." By keeping track of these user agent strings, Web traffic analysis software can create logs showing information on what percentage of users come to a site with Firefox, Safari, or Internet Explorer, for example.
Thecharacterencodingmeta tag
Many servers, but not all, indicate the character encoding in the HTTP response header. But whether or not your pages are on a server that indicates the encoding, you should do so in the document itself, by adding the appropriate character encoding meta tag to the head section. Assuming the document was encoded in UTF-8, and is using HTML 5, you simply need to add this to the <head> section:
<meta charset="utf-8">
Because this tag tells the browser how to interpret the characters used in the document, it should be the first tag in the<head> section.
The HTML validator needs to know which character set the document is encoded in so it can properly evaluate it. So if your pages are on a server that does not indicate the encoding, it is necessary to add the character encoding meta tag to your HTML or the validator may not be able to properly evaluate the page. Additionally, if your pages are not being served by a Web server (they are being viewed locally, or perhaps they are to be burned onto a CD) the browser will need the character encoding meta tag in your HTML to properly display the page.
In the case where the server indicates the encoding, and you also indicate the encoding with the character encoding meta tag, there is no problem if your tag and the file header from the server indicate the same encoding. But if the server says the encoding is, for example, ISO-8859-1, and your meta tag says UTF-8, the validator will give you a "character encoding mismatch" error. In such a situation the validator assumes the server's encoding is the one to use. In other words, in the event of a conflict between your tag and the server, the server overrides your character encoding meta tag.
How to seeaserver’scharacterencodingsetting
To see what your server says about the pages it is serving, you need a way to see its invisible file response header. A tool such as
Rex Swain's HTTP Viewer will allow you to see this, including the character encoding, if any is indicated. Go there and enter a URL for a server that you wish to check then look at the "Receiving header."
If you see something like:
Content-Type:·text/html;·charset=UTF-8
then you know the server says the documents it is serving are encoded as UTF-8.
If you see something like:
Content-Type:·text/html;·charset=iso-8859-1
then you know the server says the documents it is serving are encoded as ISO-8859-1.
If you see something like:
Content-Type:·text/html
then your server is not indicating the character encoding.
Remember that if your server does not indicate the character encoding, it is even more important that your pages contain the character encoding meta tag. This will give the browser the information it needs to properly render your page (otherwise it will have to guess at the encoding, and it may guess wrong), and it will give the HTML validator the information it needs to properly evaluate your page.
Keepeverythingin synch
To make sure the browser renders your page as you intend (so that special characters such as curly quotes, apostrophes, accented characters, dashes, etc. display properly), and to enable the HTML validator to work, it is important that the server’s character encoding setting, your page’s character encoding meta tag, and the actual character encoding of the document all match.
It is recommneded that Web pages use the UTF-8 encoding. To ensure that your pages are actually encoded as UTF-8, your text editor must be configured to save your pages as UTF-8
Setting Komodo Preferences for UTF-8 / No BOM:
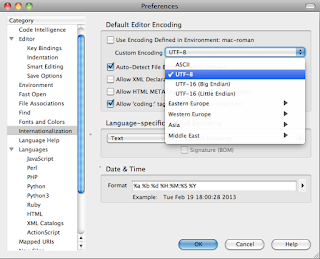 |
Launch Komodo and go to File/Preferences/Internationalization.
Uncheck the top option box to find the UTF-8 option in the pulldown menu |
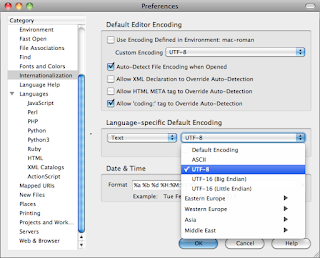 |
Change this second language-specific default encoding option to UTF-8.
Leave Signature BOM unchecked. |










